In the ever-evolving threat landscape, safeguarding sensitive data is paramount. Salesforce, a leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform, has grown into a mission-critical application for any modern business and is crucial in managing vast amounts of critical data. To ensure the security of your Salesforce data and uphold the trust of your customers and stakeholders, you must implement top-notch security practices.
In this guide, we’ll explore the top 10 Salesforce security best practices and tips and offer a comprehensive overview of strategies to fortify your Salesforce instances against potential threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
Follow these tips to fit your business needs and you will see a more secure, resilient, and trustworthy business environment that will ultimately contribute to your organization’s customer satisfaction and long-term viability.
1. Application Security: OWASP Top 10
Let’s take a look at the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10 list. This Top 10 is a periodically updated list of the ten most critical web application security risks as indicated by OWSAP, a nonprofit organization dedicated to improving security software across the ecosystem.
Being a major data management company, Salesforce regularly monitors and invests in its security measures and has many default protections for most known vulnerabilities. But there is still a short list of items that may leave you vulnerable to attacks.
These Include:
SOQL Injection: Salesforce runs its own SQL language, SOQL, which is more secure against injection attacks as it can only read data, not modify it. However, when running dynamic queries on untrusted data, an SOQL injection attack could occur that could reveal sensitive data. To avoid this, only run static queries when possible.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) enables attackers to inject malicious scripts into a victim’s browser, leading to session hijacking or web app defacement. The Salesforce platform has built-in tools for countering XSS, but developers should minimize DOM manipulation, preferring template directives; if using lwc:dom=”manual,” sanitize inputs to avoid security gaps. Additionally, avoid JavaScript functions that evaluate strings as code, and diligently evaluate third-party libraries for potential XSS vulnerabilities
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): CSRF is when a malicious actor can force an authenticated user to perform unauthorized actions on a web app. The Salesforce platform has default CSRF protections automatically enabled in the Setup menu, but there is a narrow opportunity when the page loads that can still leave you vulnerable. Salesforce recommends not performing DML operations in Lightning Web Components and load (constructor, connectedCallback, renderedCall back) instead.
2. The Principle of Least Privilege
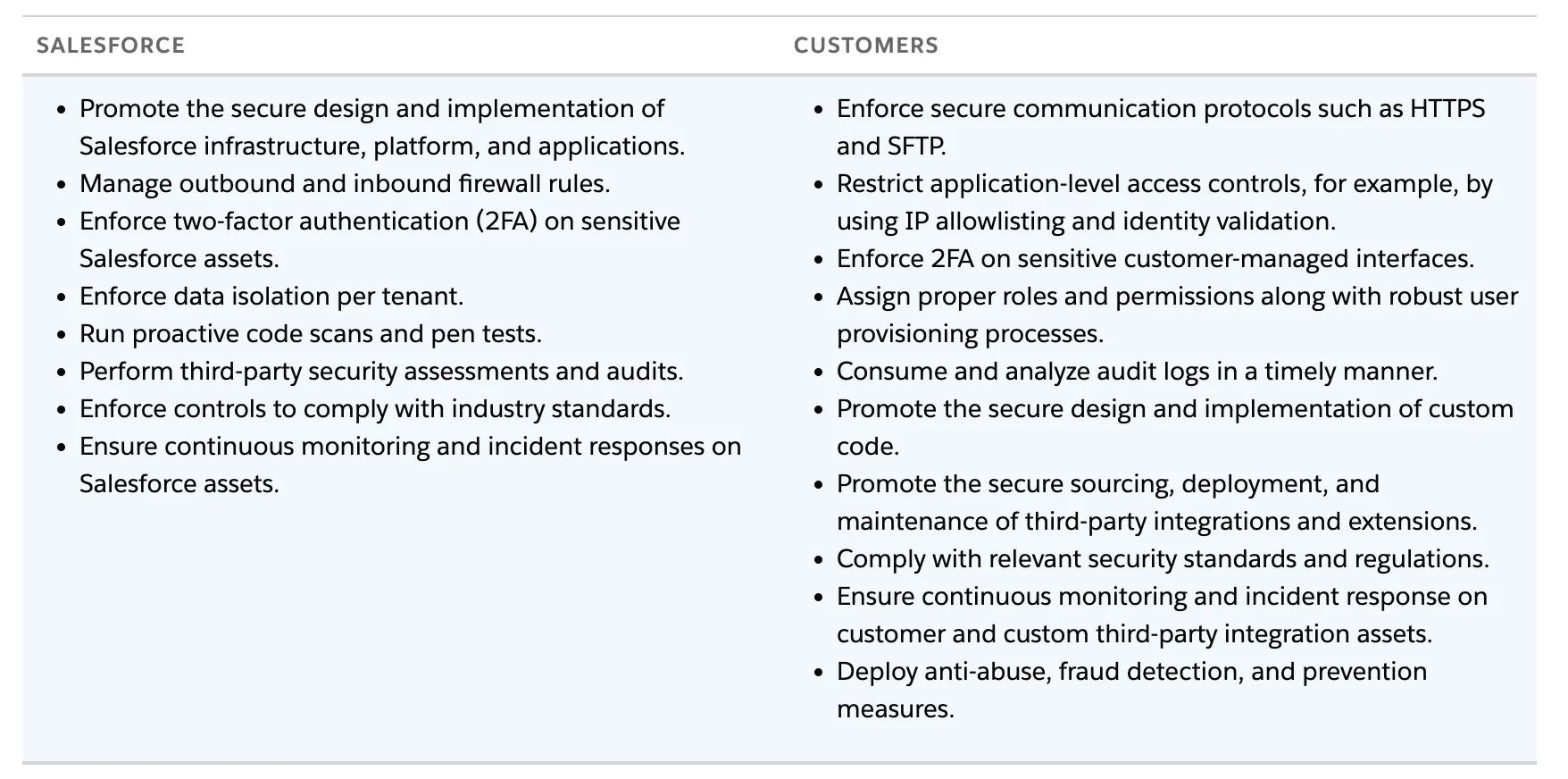
The principle of least privilege, or POLP, is a commonly used and easily implemented security concept that restricts access rights for users, accounts, and systems to the bare minimum necessary to perform their daily tasks. By implementing this basic policy, you limit the potential damage of unauthorized data leaks by minimizing the privileges granted to users and systems to high-profile data and material.
The fewer people and systems who have access to data, the fewer vulnerabilities you need to worry about.
Because Salesforce is a large, versatile platform with sprawling access to customer, sales, and marketing information, this basic first step should be considered necessary when designing your security policies.
You should start by defining specific user profiles and the kind of data they will be granted access to. If a specific kind of user needs access to data not typically related to their profile, having customizable permission sets for individual cases can help limit IT requests, but keeping things on a need-to-know basis should be the priority.
Also, remind developers to be careful when implementing custom code within Salesforce. Custom code that reaches beyond the data needed for its designed purpose will create an entryway similar to profiles with access to that data.
3. Practice Smart User Privilege Management
User Privilege Management is the systematic control and administration of permissions granted to users within a system, ensuring appropriate and secure levels of access based on roles and responsibilities.
User Privilege Management (UPM) and POLP often go hand in hand, but UPM encompasses a broader series of practices, while POLP is a guiding principle within your UPM framework.
Common user privilege management practices include actively regulating user activity permissions through record and field-level permission sets, as well as role-based access, all of which we will cover more below.
These practices fortify the platform against evolving cyber threats, providing organizations with a proactive defense strategy and safeguarding sensitive data effectively.
4. Field and Record-Level Security
Field and Record-Level Security refer to separate but related security concepts. In short, Field-level security (FLS) refers to the ability to control access to individual fields on objects or allows administrators to restrict which users or profiles can view or edit specific fields within your records.
For example, a user may have access to a report or page that may have data or information you may want to restrict them from viewing. Field-level security settings determine what kind of data on those reports or pages the user is allowed to see.
Admins can configure field-level security settings for each field subject through the Salesforce Setup menu. Once there, administrators can make fields read-only, hidden, or visible/editable based on user profiles.
Record-level security (RLS) access to entire records based on certain criteria. It determines which users or groups of users can view, create, edit, or delete records based on conditions such as ownership, role hierarchy, or shared roles.
A common example for sales operations is implementing record-level security to ensure sales representatives can only access and modify records related to their assigned accounts.
Salesforce’s Record-Level Security (RLS) offers multiple implementation options, such as Role Hierarchy, where organizational hierarchy defines access levels; Sharing Rules, applying criteria-based rules for automated access extension; Manual Sharing, enabling record owners to share with specific users or groups manually; and Team-Based Security, allowing users to be assigned to teams with record sharing at a team level.
5. Role-Based Access
Role-based access control, or RBAC, is a hierarchical security practice that involves assigning access permissions to users based on their roles within your organization.
In this system, users are grouped into roles that mirror the structure of your company. Access permissions are then defined for each role, determining the data and functionalities users in those roles can access. Typically, users at the top of the hierarchy, like executives or upper management, have access permissions to all files, data, objects, and/or pages below them, while lower-level users only have access to information found on their level. Salesforce’s RBAC system allows for the creation of such hierarchies, helping to facilitate a structured and efficient access control model for your organization.
Overall, RBAC ensures users have tailored access to information and features relevant to their jobs and responsibilities.
6. Multi-Factor Authentication
Since 2022, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has been required for Salesforce users, and it is a commonly implemented security protocol across the digital ecosystem. This means users must verify their identity twice or more as they log in to their accounts.
In Salesforce, where sensitive customer data and business information are stored, requiring multiple verification forms adds an extra layer of data protection against unauthorized access and data breaches. This way, even if a password is compromised there is an additional factor required for access, mitigating the risk and impact of phishing or other credential-based attacks.
Below we have listed the number of ways the Salesforce platform allows you to verify your identity before logging into your account:
- Salesforce Authenticator App: a downloadable mobile app that will generate a unique one-time code users must enter at login, similar to Google Authenticator
- SMS or Email Verification: Users will receive a verification code via SMS or email that they must enter during login
- Biometric Authentication: Users must authenticate using biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition via built-in authenticators on their mobile devices.
- Hardware Tokens: A physical device, typically a key-chain-like token, that periodically generates a unique code that must be entered during login.
7. Data Backup Strategies
Salesforce is one of the most secure mission-critical platforms on the market, but that doesn’t mean it’s invulnerable to threats like human error, system failures, data corruption, or errors from customization and development.
Keeping a robust and regular backup system will give you peace of mind against any unforeseen and unexpected circumstances while also ensuring the continuity of your business operations.
To back up your Salesforce data, utilize the platform’s native tools and features designed for data export. The Data Export tool enables you to schedule automatic exports and customize the frequency and types of data to be included.
Additionally, Salesforce’s Weekly Data Export service provides downloadable backups of your entire Salesforce instance, including standard and custom objectives.
To maintain compliance, uphold Saleforce’s Service Level Agreement, and ensure the highest quality of security for your organization and clients, your data should be encrypted in transit and upon delivery to the backup device or server.
Salesforce products provide a variety of platform encryption options, including encryption in transit using secure communication protocols (TLS/SSL) and encryption at rest for Salesforce data stored in their databases. Additionally, when choosing external storage solutions, such as cloud storage or third-party backup services, make sure that they offer encryption features to protect your backup files.
8. Implement Continuous Security Monitoring
Continuous security monitoring is a crucial component of any comprehensive security strategy. This approach involves systematic and real-time observation of your user’s/system’s permissions and behaviors to detect security breaches and vulnerabilities promptly and allow for a real-time response.
Implementing a continuous security monitoring system in the Salesforce environment requires a proactive and comprehensive approach to safeguarding data and operations. Start by enabling Salesforce Event Monitoring, a feature that logs a broad spectrum of user activity and system events. Define and prioritize key security events relevant to your organization, such as login anomalies, configuration changes, or access to sensitive data. Then leverage Salesforce’s reporting and dashboard capabilities to create custom reports and visualizations for monitoring these events.
You can then automate alerts and notifications based on predefined security rules to receive immediate notifications of potential threats.
Afterward, you will want to engage in continuous employee training and awareness programs to cultivate a security-conscious culture.
Luckily, Salesforce’s Trailhead courses offer account holders a Security Awareness Module to help teach employees the importance of cybersecurity and how to identify risks.
9. Regular Security Audits and Health Checks
Because you may be implementing various strategies to protect your Salesforce data, instances, customer information, and mission-critical applications, you will want to maintain regular surveillance of your security vulnerabilities to ensure the safeguarding of your and your customer’s data.
Regular, ideally annual, Salesforce health check and security audits will allow you to keep things up to date and make sure you are following any regulatory compliance requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) for your clients, as well as allowing you to track your incident response preparedness and system configuration overview.
An effective security health check that reveals your current Salesforce Configuration should consist of the following:
- Review User Access and Permissions/Checking For Inactive Users
- Review Sessions Settings
- Examine Password Settings
- Inspect Network Access Controls
- Examine Data Loss Prevention Policies
- Check For Any Salesforce Updates
- Document And Report Your Findings
- Educate Your Users
- Engage With Salesforce Support
10. Use a SaaS Security Tool
Incorporating a Software as a Service (SaaS) security tool into Salesforce is essential for fortifying the platform against evolving cyber threats and ensuring the integrity of sensitive data. A dedicated SaaS security tool offers your security team advanced threat detection, real-time monitoring, and proactive response mechanisms that go beyond the many native security features of Salesforce.
SaaS security tools like SpinOne provide an additional layer of defense, detecting anomalies, unauthorized access, and potential vulnerabilities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
With the complexity of modern cybersecurity challenges, a specialized SaaS security tool enhances your organization’s ability to meet compliance requirements, safeguard customer information, and maintain a resilient security posture. It also allows for centralized security management and integration with broader security ecosystems, providing a comprehensive and adaptive security strategy tailored to the unique needs and risks associated with Salesforce deployments.
For more information, schedule a free demo here.
Thanks for your feedback!