How to Achieve Seamless Compliance and SaaS Security Control
- Why compliance and SaaS security in cloud environments is challenging
- Why is monitoring user activities important to compliance and SaaS security?
- SaaS Application compliance and security concerns
- Before you install apps
- Protecting and regulating data access
- Shadow IT concerns
- Seamless compliance and SaaS security control with SpinOne
Cloud Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) environments provide businesses with modern tools and cloud-centric connectivity to empower end-users. As a result, many companies have migrated to services like Google Workspace and Microsoft Office 365, especially since the onset of the global pandemic. However, as businesses have migrated business-critical services to cloud services, compliance and SaaS security issues quickly come to the forefront.
Traditional on-premises tools no longer provide visibility into users, data, and applications across, often multiple, SaaS environments. As a result, data security, data access management, anomaly detection, and immediate response in the cloud can also present challenges.
This overview of SaaS compliance will look at why compliance, visibility, and security are vital in cloud SaaS environments and areas of importance for your organization.
Why compliance and SaaS security in cloud environments is challenging
Organizations today are leveraging cloud SaaS more than ever. In fact, SaaS adoption is far outpacing cloud IaaS adoption. Cloud service providers enable businesses to move with agility and access modern and robust infrastructure, services, and applications. However, many organizations transition over to cloud SaaS environments and realize they no longer have tools to monitor end-user activities, data locality, external data access, and third-party application integration into the environment.
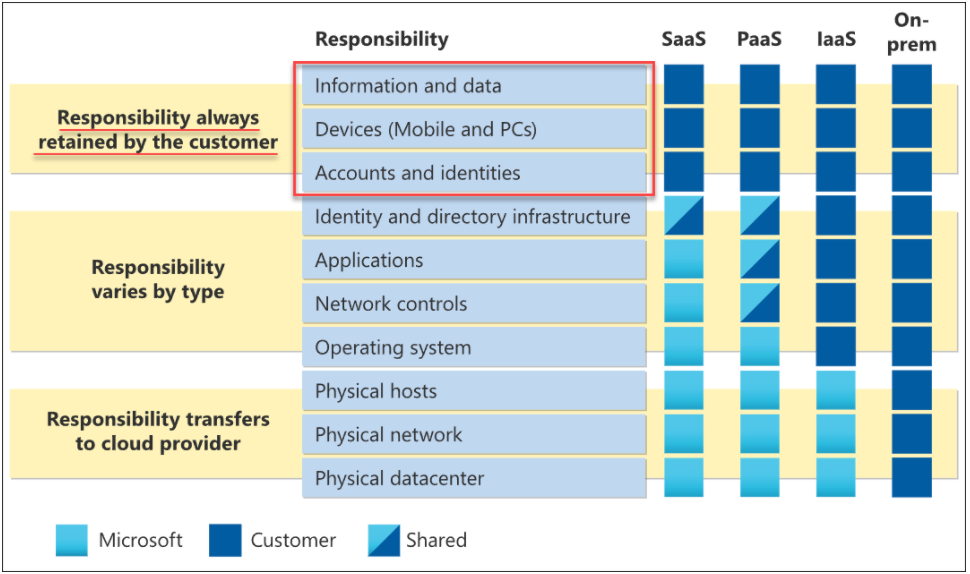
What’s more, compliance regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and SOX do not go away when data moves to the cloud. Businesses may incorrectly assume that compliance becomes the responsibility of the cloud service provider. However, as shown in the Microsoft infographic, compliance and security responsibility of information and data ultimately rests with the customer.
Cloud SaaS shared responsibility model
Businesses often find the native tools provided by cloud service providers lack the visibility and features they need and are often disjointed between the different individual services within the same cloud SaaS environment, each using a different security interface. In addition, many of the security and compliance features may even depend on the customer’s subscription level.
Compliance and cybersecurity concerns and areas of focus for cloud SaaS environments generally fall into one of the following categories:
- User activities – For proper compliance and security visibility, organizations need to have visibility to end-user activities and know what users are doing, what data they are accessing and sharing, and where and on what devices they are accessing it.
- Applications – There is a myriad of third-party applications that can integrate into the cloud SaaS environment. While these can be beneficial, they also introduce cybersecurity risks into the environment. As a result, organizations must have the ability to monitor and control the use of third-party applications.
- Data – Data is the most valuable possession of modern businesses. As a result, companies must protect their business-critical data from many different risks, including human error and malicious threats such as ransomware.
- Shadow IT – Cloud SaaS environments are often a breeding ground for shadow IT operations among end-users, given the ease with which users can integrate third-party applications and share data.
What essential questions do organizations need to consider for their cloud SaaS environments’ compliance and overall cybersecurity? Note the following:
- User activities
- Who is downloading sensitive data to unmanaged devices or sharing data outside the organization?
- How can I monitor and govern user activities that appear suspicious?
- SaaS applications
- How many SaaS applications are used in the sanctioned cloud SaaS environment?
- Which SaaS applications are the riskiest ones and can potentially hurt my security and compliance frameworks?
- Data governance and security
- Who uses file-sharing services, and how can the compliance and security challenges be addressed?
- What are the most dangerous SaaS data leakage sources across my SaaS environments, and what automated action can be taken to prevent that?
- Shadow IT
- How can I discover Shadow IT applications and centrally assess, control, and enforce user, data, and security policies?
Why is monitoring user activities important to compliance and SaaS security?
The whole purpose behind a cloud SaaS environment is to enable users to communicate, collaborate, and share resources effectively and efficiently. However, when it comes to compliance and security, organizations need to understand user activity and recognize anomalies in user behavior patterns as this can be an indicator of compromise (IOC).
The overall goal of monitoring user activity is to protect business-critical data while ensuring compliance with data privacy and security regulations. Many compliance regulations require monitoring many areas of the business-critical infrastructure, including areas related to end-user activities. Note the following types of monitoring that relate explicitly to user activity:
- Threat monitoring
- Event logging
- Access logging
Threat monitoring
A specific type of monitoring often required for compliance is threat monitoring. With threat monitoring, organizations attempt to determine if a possible insider threat exists with a particular user or there is perhaps a compromised account showing signs of anomalous activity.
Traditionally, this has often been carried out by the SecOps team using manual processes. However, this approach is no longer feasible or effective with cloud services’ sheer width and scope. Businesses today often need to use automated assessments and threat monitoring that uses artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML) to perform low-level monitoring effectively.
Without third-party tools, businesses may find it challenging to have effective threat monitoring, and most legacy solutions do not integrate with or monitor cloud environments.
Event logging
The key to effective monitoring for compliance and security is proper event logging. Effective cloud SaaS event logging captures and aggregates audit events across cloud SaaS services. What information should organizations capture with a monitoring solution? Organizations should monitor and capture events, including:
- Applications installed and revoked
- Data sharing, revoked sharing permissions, files edited, deleted, and permissions changed
- Data downloaded from cloud SaaS storage
- Logins – successful and unsuccessful
- Sensitive data access and transmission
Many of the native compliance and auditing solutions found in cloud SaaS environments can make it difficult to view all auditing and security events in a single location. Also, as mentioned earlier, the range of security features enabled may depend on the subscription level purchased for the cloud SaaS subscription.
Access logging
Access monitoring is a specific type of monitoring to see which users or other entities are accessing which resources. It includes users’ access to various resources, including files, folders, applications, and other cloud SaaS resources. In addition, it should also capture application access to resources. Thus, it provides visibility to which users and applications are accessing which data.
SaaS Application compliance and security concerns
One of the benefits of migrating services to cloud SaaS environments is the wealth of third-party application integrations available. For example, both Google Workspace and Microsoft Office 365 have thousands of app integrations available. It allows businesses to easily extend the native functionality of the cloud SaaS environment with third-party solutions. In addition, third-party browser extensions can also easily integrate with your cloud SaaS environment.
However, having an external application granted access to your business-critical and potentially sensitive data can lead to many concerns regarding compliance and security. Third-party applications integrated with the cloud SaaS environment can easily read, write, and delete sensitive data, compromising cybersecurity and compliance.
Organizations must assess the risks of third-party applications when maintaining the balance between the security and productivity of end-users. In fact, Google, as does most cloud service providers, shifts the responsibility to screen applications to your business. Note Google’s published guidelines to evaluate a Google Workspace Marketplace app:
Before you install apps
The developer is responsible for supporting their app. They are responsible for ensuring that it works well for you and your users. To help you determine if an app is trustworthy before you install it from the Marketplace or allowlist it, on the app’s listing page you can review:
- Information in the Overview tab about the developer and the app, such as the Google Workspace products the app works in, its details, and screenshots
- The developer’s Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and any other information provided in the Additional Information section
- Permissions that the app is requesting in the Permissions tab to ensure that these meet your organizational policies
Note: For assistance with an app, reach out to its developer directly using support channels provided in the app listing.
As Google outlines, organizations must take ownership of evaluating all vendors and applications before using them. It means that businesses must have controls in place that prevent end-users from simply installing a marketplace app in an unsanctioned way without vetting it for security and compliance alignment.
Attackers are beginning to turn their attention to cloud SaaS environments as they realize there is a tremendous shift to cloud SaaS for modern productivity. With the default permissions and controls from the cloud service provider, end-users can easily integrate third-party applications. All it takes is consenting to the OAuth authorization prompts to install the application.
For example, attackers can persuade a user to install a malicious application by passing this off as legitimate using a phishing email. If the organization has no controls to prevent this, the attacker can quickly assume the permissions granted to the user to read, delete or leak sensitive data.
A disgruntled user can quickly integrate a third-party file sharing app into the business environment and easily download corporate data to their personal cloud environment. Again, organizations must have the visibility, controls, and policies that tightly control the integration of third-party applications with the sanctioned business environment.
Protecting and regulating data access
Of primary concern for security and compliance is data. Business-critical data can include any number of things, including customer information deemed sensitive by regulatory compliance frameworks today, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Sensitive data is highly lucrative on the dark web, and hackers have made this one of their prime targets as they attempt to compromise environments. Aside from obvious sensitive data such as credit card numbers and social security numbers, attackers are targeting the personal information of customers – names, addresses, phone numbers, and other PII data.
As discussed, when no controls are in place, users can easily integrate third-party applications into cloud SaaS environments. In addition to the threat posed by risky third-party applications, cloud SaaS environments also make it extremely easy to share data, both inside and outside the organization.
Organizations must have clear visibility to:
- Who is accessing data
- Where data is located (data locality)
- How their data is shared in the cloud SaaS environment.
Failure to have these types of visibility on your data can easily result in data leaks. A data leak, either intentional or unintentional, can cost your businesses millions of dollars. According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021, the average cost of a data breach has risen to $4.24 million. The 2021 figure is the highest cost of a data breach since the report was first released 17 years ago.
Many organizations find it challenging to use native cloud SaaS admin tools to see how their data is accessed and shared across the multiple services a user may be accessing. As a result, organizations find that third-party solutions are required to achieve the visibility and “single view” of data access and sharing.
Shadow IT concerns
Tying in closely with the concerns over application security, detailed above, is shadow IT. What is it? Shadow IT is any hardware, software, service, application, or otherwise, the user is using to access or interact with sanctioned business-critical data without the consent or approval from IT. Cloud SaaS has made it effortless to easily connect apps, tools, and third-party solutions with the business environment. In just a few clicks or taps on a smartphone, users can integrate and start using applications that are not sanctioned or expressly allowed by the organization.
Some may even be unaware they are becoming involved in shadow IT operations. However, many well-meaning users want to have the tools to carry out business tasks and processes more efficiently and effectively. Shadow IT operations can even unfold at a departmental level as certain departments or divisions may want to use a specific application to assist with a departmental-specific challenge or task.
As many department heads are approved to make purchases without additional approvals, buying into a SaaS application can be as simple as entering a credit card number. Unfortunately, this workflow and ease of SaaS application integration have led to an explosion of unsanctioned applications that have recently been referred to as Shadow SaaS.
It underscores the importance of discovering, auditing, monitoring, and controlling all cloud SaaS applications integrated with the environment. Unfortunately, businesses usually find the native cloud SaaS tools inadequate in providing the visibility needed. Third-party solutions can help close the gap on shadow IT concerns in the cloud.
Seamless compliance and SaaS security control with SpinOne
As described, the challenges with modern compliance and cybersecurity concerns in cloud SaaS highlight the shortcomings of the built-in tools provided. As a result, businesses often find the security and compliance tools challenging to use and lack the visibility and controls provided.
SpinOne is a modern SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM) platform that provides robust tools for both cybersecurity and compliance in a modern cloud SaaS environment, including Google Workspace and Microsoft 365.
Business risk, security risk, and compliance risk assessment must be a part of your cybersecurity strategy. SpinOne’s SpinAudit provides automated evaluations of applications and user behaviors, leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
SpinOne allows organizations to audit user activity, review application utilization and data access in real-time, and maintain records for compliance. With SpinOne, you can create custom policies to automate the security processes for SaaS apps, data, and domain-related activities.
It provides organizations with the following capabilities:
- 24/7 monitoring
- Security policies
- Security scoring for apps and browser extensions
- Audit logs and activity history
- Blocklist of apps and browser extensions
- Security alerts via email and slack
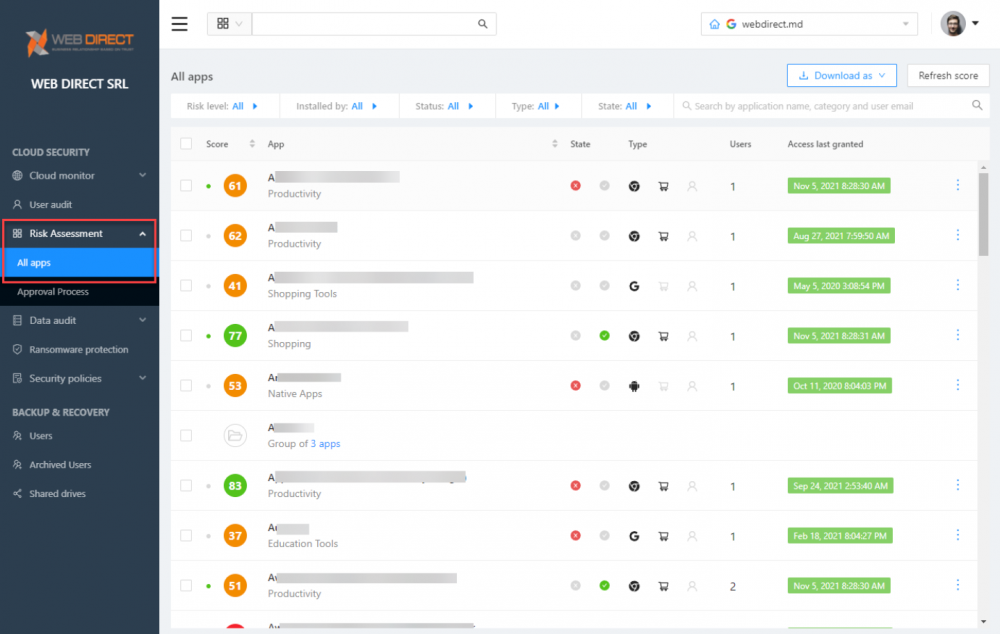
SpinOne automated risk assessment dashboard provides continuous automated SaaS application scoring
Find out more about what Spin can do for your organization, including how you can strengthen your cybersecurity and compliance posture for your cloud SaaS environment by clicking here.
Was this helpful?
How Can You Maximize SaaS Security Benefits?
Let's get started with a live demo
Latest blog posts
Midnight Blizzard Attack on Microsoft: Key Lessons for Strengthenin...
Midnight Blizzard Attack on Microsoft: Key Lessons for Strengthening Your SaaS Security From November 2023...
Why a Reliable Backup Plan is Your Best Defense Against Cybersecuri...
…and the Most Boring Way to Protect Your Organization I’ve written about the importance of...
Why Google Drive Backups Are Important
Google Drive offers customers a unique blend of robust security features to keep their data...