Cybersecurity Risk: Definition, Management & Assessment
What is cybersecurity risk?
Cybersecurity risk is a negative outcome that an organization may endure in the event of a cyber incident occurrence in its digital ecosystem.
Another common understanding of this term is the probability of a cyber incident happening in an information system.
Types of cyber risks
By probability:
- Unlikely, e.g., the infection with an old virus
- Likely, e.g., data breach through shadow IT.
- Highly probable, e.g., a ransomware attack.
By impact on an organization:
- Non-harmful, e.g., the exposure of non-sensitive data to third-parties.
- Harmful, e.g., the deletion of files in the absence of data backup.
By area of impact:
1. Architectural.
The damage to the organization’s information system and its components. For example, physical damage to data storage.
2. Procedural.
The disruption of business operations. For example, the inability to communicate with clients due to the outage of Google services.
3. Data.
The unauthorized access causing data leak, loss, or corruption. For example, the encryption of data stored on a cloud drive.
4. Legal.
The breach of law causing legal proceedings against an organization. For example, a lawsuit for the exposure of PII.
5. Reputational.
The harm to a company’s public image, the undermined trust of clients, coworkers, and partners. For example, a scandal in mass media after a cyberattack was made public.
6. Financial
The money losses due to downtime, lawsuit, the costs of recovery. For example, the payment of a ransom to get the decryption key.
7. HR
The psychological impact of cybercrime on the organization’s employees. For example, after exposure to their sensitive information, employees feel anxiety and reluctance to work.
In most cases, a single cyber incident bears multiple risks rather than one.
Risk Management
Cybersecurity risk management is the body of policies, activities, and tools that help an organization prevent, minimize, or defend against cyber incidents.
Risk Management Step-by-Step:
- Assess the risk by the chosen criteria;
- Choose the management approach;
- Create the rule/policy for dealing with this risk;
- Implement the policy/rule;
- Monitor, analyze, and change the approach or policy if necessary.
Cyber Risk Assessment Criteria:
- The probability in %;
- The areas of impact;
- The severity of a cyber incident in %;
- The duration of outcomes in days;
- The cost of incident occurrence in $.
More about risk assessment.
The Strategies for Cybersecurity Risk Management:
1. Acceptance
The cybersecurity team knows about the risk but takes no action because the probability is low, the cost of mitigation is high or the preventative actions are incompatible with key business processes.
For example, a company doesn’t raise its staff awareness on cybersecurity threats because they lack resources for it.
2. Avoidance
The cybersecurity team determines to avoid practices and tools that bear cybersecurity vulnerabilities and might cause a cyber incident. For example, employees aren’t allowed to install any applications, programs, or extensions on their working computers.
3. Transfer
An organization shifts the entire liability and responsibility or a part thereof for the risk occurrence on another organization. For example, they purchase insurance. However, not all industries are allowed to do so.
4. Mitigation
This is a proactive approach to risk management that encompasses the following:
- The constant search of vulnerabilities and decrease of surface attack
- Tools and practices for incident prevention, detection, and removal
- Playbooks for incident occurrences.
- Tools & procedures for damage minimization and recovery.
An example of risk mitigation would be using SpinRDR. It’s a tool that detects a ransomcloud attack on Google Workspace, stops it, and recovers the encrypted files.
A single company can apply multiple strategies depending on the risk and how they assess it.
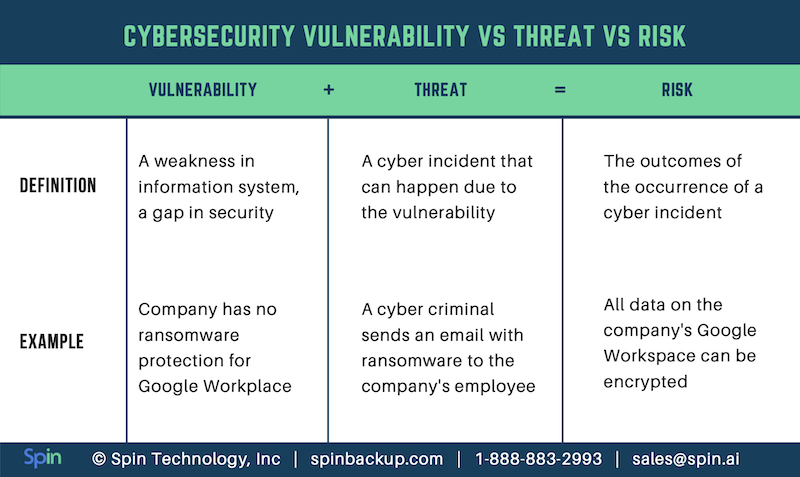
Don’t confuse cyber risk, threat, and vulnerability
Check out the difference in our table:
Was this helpful?
How Can You Maximize SaaS Security Benefits?
Let's get started with a live demo
Latest blog posts
Why Google Drive Backups Are Important
Google Drive offers customers a unique blend of robust security features to keep their data...
Evaluating the Best Backup Services: What to Look For and Popular O...
If you’re here right now you’ve probably realized how important it is to backup your...
Brewing Trouble: How a Starbucks Ransomware Attack Poured Cold Wate...
Cybercriminals often carry out attacks around holidays as this helps to ensure the most amount...


