Ransomware Double Extortion: How to Protect Your SaaS Data
On top of just about any, cybersecurity threat list is ransomware. Ransomware continues to plague businesses worldwide, and this trend is not showing any signs of slowing down. Ransomware continues to devastate organizations, even those who are seemingly prepared. Ransomware gangs continue to evolve their tactics to profit even further from victimizing unsuspecting businesses with ransomware, even using “double extortion.” What are the basics of the ransomware double extortion “business model?” What is this double extortion tactic? How can companies protect modern cloud SaaS data from falling victim to new ransomware threats?
The ransomware business evolution
Let’s key in on the business model used by ransomware gangs to make millions of dollars from major organizations. When ransomware first appeared on the scene, it was known as a single PC, single user type threat. Ransomware would lock up a victim’s files and demand a ransom payment to restore access.
Now, ransomware is a multi-billion dollar industry that is a high-profit, low-cost attack that is alarmingly successful. However, due to the successful beginnings and evolving business model, attackers have set their sights on much more lucrative enterprise targets, a change in tactic that has proven wildly successful.
Sophisticated ransomware attacks are rarely the result of a “lone wolf” actor. Instead, modern ransomware attacks are perpetrated by groups of individuals with different levels of involvement in the overall attack on an organization. This involvement may include the initial reconnaissance, providing the credentials to infiltrate the victim organization, exfiltrating data, and encrypting data.
The success and sophistication of today’s ransomware have led to Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS). With RaaS, even non-technical, amateur criminals can carry out a successful attack against a business, using the tools available and provided by ransomware gangs.
Microsoft’s Digital Defense Report 2021
According to Microsoft’s Digital Defense Report 2021:
“Among the services available to even amateur threat actors are the cryptocurrency escrow services (to ensure services are rendered as offered) that we often see in commodity ransomware campaigns where affiliate models have become firmly established. Nontechnical cybercriminals sign up with a ransomware affiliate where for 30% of the revenue, the affiliate network will supply the ransomware, recovery services, and payment services. The attacker then buys “loads” from a market and pushes the ransomware to the loads they purchased. They then sit back and collect their revenue.”
In addition to payment services, underground cybercrime organizations are creating specialized kits and services that other actors can buy and use for their own malicious campaigns. One of the services offered on the dark web is backconnect proxies.
The backconnect proxies are servers that rotate through a pool of residential proxies and switch between these different connection points after a short time. It makes the connections much harder to track and offers better anonymity for attackers for malicious purposes.
A trending service on the dark web is the Initial Access Broker (IAB). The IAB serves as a middle man to ransomware gangs looking to attack an organization. The IAB uses its own methods to breach and compromise organizations. They harvest credentials and sell these on the dark web. Ransomware gangs simply purchase the credentials they are looking for and use the compromised credentials to launch an attack.
These factors and many others have proliferated the use of ransomware across the globe for compromising large organizations and their business-critical data.
An intelligence operation
The actions and tactics of cybercriminals using ransomware to attack victim organizations can be described as an “intelligence operation.” The attacker carefully performs research on the victim organization to decide the optimal ransom demand.
The attacker does not immediately launch the ransomware attack. Instead, they may carefully study sensitive financial information discovered in the victim network, any cyber insurance policies the victim looks to have, and also local breach laws and compliance penalties to extort money from the victims.
Ransomware double extortion
Ransomware gangs are continually evolving the business model and making even more money from an attack. Previously, ransomware gangs were attacking businesses, locking up their data, and demanding ransom payment. However, there has been a shift in how ransomware gangs carry out operations during an attack.
Rather than only locking up a victim organization’s data and demanding a ransom payment for regaining access to business-critical files, attackers are also exfiltrating sensitive data BEFORE encrypting the data. This activity serves two purposes.
It includes:
- Preventing a victim organization from breaking off negotiations, especially if these have good backups of their data
- It allows effectively carrying out “double extortion” on victims
As stated in the blog – How cyberattacks are changing according to Microsoft Digital Defense Report:
“Once a criminal actor compromises a network, they may steal confidential information, financial documents, and insurance policies. After analyzing this intelligence, they will demand an “appropriate” ransom to not only unlock their victim’s systems but also to prevent public disclosure of exfiltrated data. This is known as the double extortion model: a victim is extorted for ransom on stolen data and intellectual property (IP), and then again to prevent the attacker from publishing it.”
This new double extortion tactic is highly alarming to businesses. The previous stance of reactively dealing with a ransomware attack, removing the threat actor from the system, and restoring your data is no longer good enough. The damage and compliance implications for businesses thinking about sensitive data leaked to the web can be catastrophic.
According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach 2021 report, note the following statistics:
- The average total cost of a data breach increased 10% from last year
- The average cost of a data breach is $4.24 million
- Healthcare has the highest cost of a data breach at $9.23 million (29.5% increase from last year)
- The average cost per record stolen was $161
- The cost of PII data stolen is $180 per record
When you consider the high cost of compliance violations from such compliance frameworks, these costs can be staggering. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) can fine organizations up to €20 million, or in the case of an undertaking, up to 4 % of their total global turnover of the preceding fiscal year, whichever is higher.
With the prospect of suffering the aforementioned costs of a data breach and subsequent fines, attackers can effectively extort money from their victims to unlock their systems AND prevent disclosing victims’ exfiltrated data to the public.
The massive growth of ransomware attacks
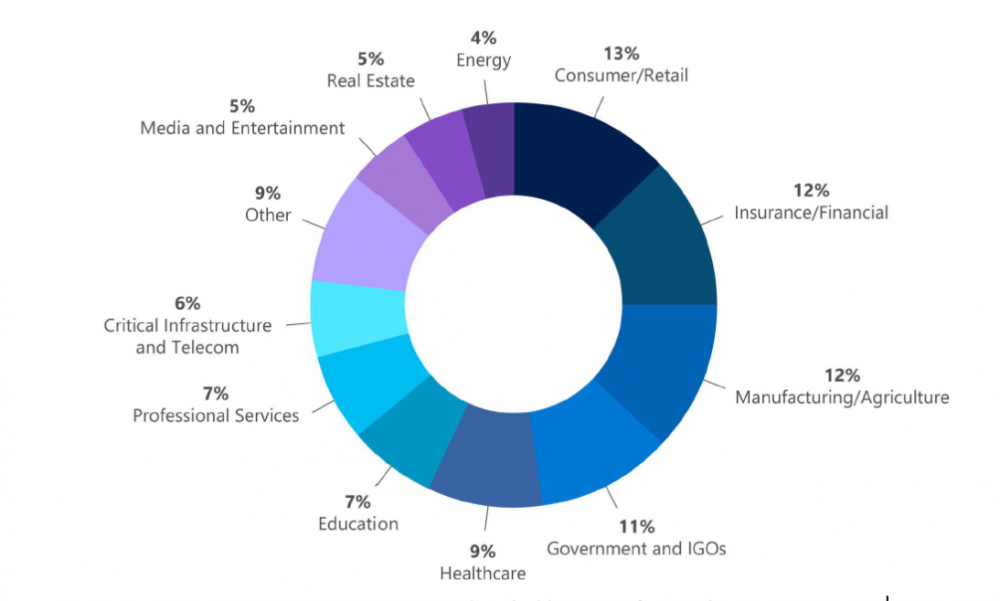
In the recent release of Microsoft’s Digital Defense Report FY2021, they noted their Detection and Response Team (DART) had seen a massive growth trajectory for ransomware and extortion. The most targeted sectors were consumer, financial, and manufacturing. Healthcare remains in the top five industries victimized by ransomware.
Ransomware engagements as detailed by DART from July 2020-June 2021
Recommendations to protect against ransomware
Microsoft recommends a three-step approach to protecting against ransomware and extortion. These recommendations include:
- Prepare a recovery plan
- Limit the scope of damage
- Make it harder to get in
1. Prepare a recovery plan
Organizations must realize it is not “if” but “when” a ransomware attack will happen. Every business is a potential ransomware victim. Therefore, companies must deploy effective ransomware protection and prepare a recovery plan. It includes making it more difficult for attackers to access and disrupt business-critical systems. By doing this, it helps to reduce the monetary incentive for attackers.
Ransomware protection and recovery plans should include cloud SaaS environments, which increasingly house a large portion of business-critical data and services.
2. Limit the scope of damage
By using cybersecurity best practices, organizations can limit the scope of damage resulting from ransomware extortion attacks. It includes establishing least-privilege access and zero-trust principles. Using least-privilege principles and micro-segmentation in the network makes it harder for attackers to freely travel “east-west” across a compromised network to find valuable data.
Organizations can also use encryption as a strong cybersecurity defense by encrypting any data at rest so that even if attackers can exfiltrate the data, it is encrypted. This step all but eliminates any leverage attackers have for double extortion.
3. Make it harder to get in
Organizations need to use good cybersecurity hygiene such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) to help prevent unauthorized access to business-critical systems, including cloud SaaS. For example, even if a user password is compromised, MFA prevents the attacker from having all the information needed for logging into the environment.
Other things such as vulnerability scanning, regular security patching, and remediating environment configurations according to desired state help bolster an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
Proactive Ransomware Protection for cloud SaaS
Times have changed for businesses using traditional reactive cybersecurity for dealing with ransomware. Unfortunately, the results can be catastrophic when organizations simply react to ransomware by thinking they will just restore data. Ransomware gangs’ new double extortion tactic means businesses must proactively protect and stop ransomware before malicious processes exfiltrate data. Backups alone are not enough. However, your organization needs a good backup strategy and efficient tools.
SpinOne provides proactive cybersecurity and data protection capabilities to organizations whose data is housed in cloud SaaS environments, such as Google Workspace Ransomware Protection and Office 365 Ransomware Protection. SpinOne leverages next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to stop ransomware and automatically remediate the damage it causes.
The ransomware protection provided by SpinOne, a fully automated SaaS security orchestration platform, includes:
- Scans for signs of ransomware in the cloud SaaS environment
- Automatically blocks the malicious ransomware process at the network level
- Scans for files affected by the ransomware process
- Automatically restores files affected by the ransomware
- Automatically alerts administrators
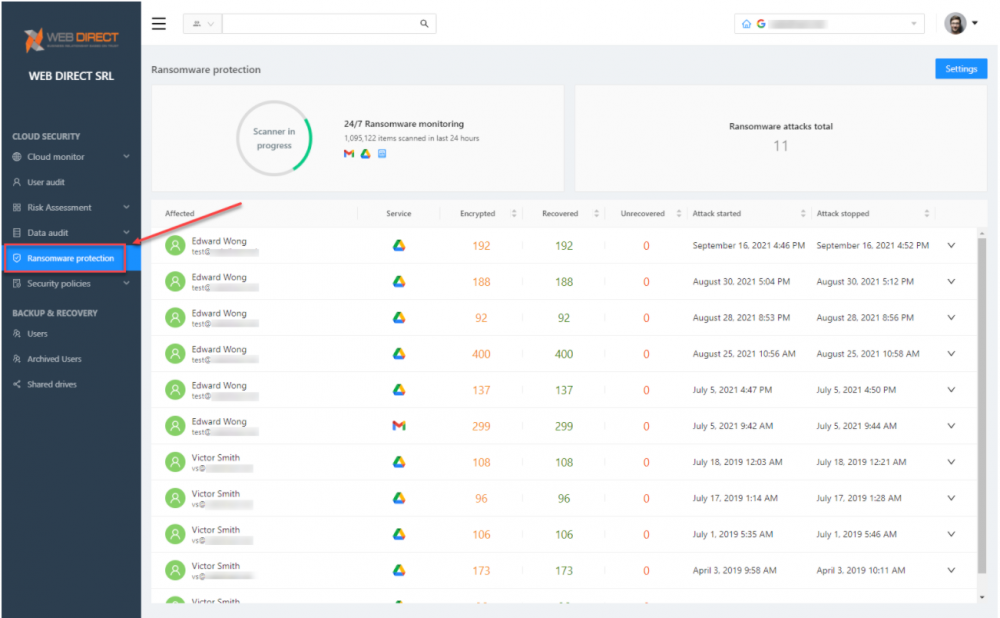
SpinOne Ransomware Protection
Organizations can configure granular ransomware protection policies to control SpinOne cybersecurity automation in the cloud SaaS environment.
Protecting SaaS data in cloud services like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce is your responsibility. Stay safe and schedule a demo here.
Was this helpful?
How Can You Maximize SaaS Security Benefits?
Let's get started with a live demo
Latest blog posts
Why a Reliable Backup Plan is Your Best Defense Against Cybersecuri...
…and the Most Boring Way to Protect Your Organization I’ve written about the importance of...
Why Google Drive Backups Are Important
Google Drive offers customers a unique blend of robust security features to keep their data...
Evaluating the Best Backup Services: What to Look For and Popular O...
If you’re here right now you’ve probably realized how important it is to backup your...